Or, “Design Constraints and Creativity”
Origami is another of my hobbies and it is all about design constraints. 1 The rules are simple2 – one square sheet of paper only manipulated by folding. 3 Yet, within these rules it is theorized that a sufficiently skilled artisan can design and fold any arbitrary figure. I find folding origami to be at once cathartic and contemplative. 4
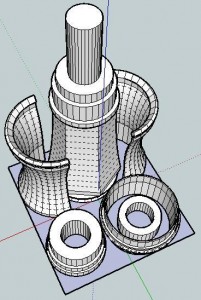
Pondering the design constraints within origami reminded me of one of my own recent designs – the 3x2x1 Rubik’s style puzzle cube. Quite apart from the medium or subject matter, I really liked the idea of a single print job resulting in parts that could be immediately hand-assembled without tools to form a useful object. Then I thought – if the design constraints are one of the things I like about this design, what else is possible within these same constraints?
Thus, I propose a new style of “MakerBot Origami”: One MakerBot print5 , multiple components6 , no tools or hardware7 .
What’s the coolest most awesome thing you can design within these constraints?
Update: Cyrozap – sory fore mispellnig yoru mane.
- I waffled on that title. [↩]
- Modern origami rules, anyhow. [↩]
- Designing an origami model is not about figuring a way to cheat those rules – rather a way to work within them to achieve a desired goal. [↩]
- I recall one origami master referring to the folding of a particularly difficult and rewarding model as invigorating. [↩]
- Or, as Cryozap Cyrozap calls them, “production file.” [↩]
- Otherwise, people would be making whistles. [↩]
- Thus, no bottle openers [↩]